How security policies work
Security Center automatically creates a default security policy for each of your Azure subscriptions. You can edit the policies in Security Center or use Azure Policy to do the following:
◈ Create new policy definitions.
◈ Assign policies across management groups, which can represent an entire organization or a business unit within the organization.
◈ Monitor policy compliance.
Edit security policies
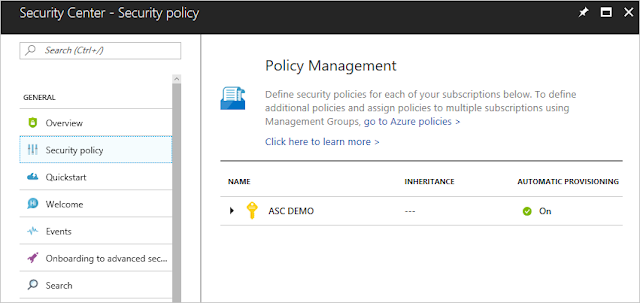
You can edit the default security policy for each of your Azure subscriptions in Security Center. To modify a security policy, you must be an owner, contributor, or security administrator of the subscription or the containing management group. To view your security polices in Security Center, do the following:
1. Sign in to the Azure portal.
2. On the Security Center dashboard, under General, select Security policy.
3. Select the subscription that you want to enable a security policy for.
4. In the Policy Components section, select Security policy.
The Basics window opens.
5. To delete a policy definition, under Policies and Parameters, next to the definition you want to delete, select Delete.
6. Click Save.
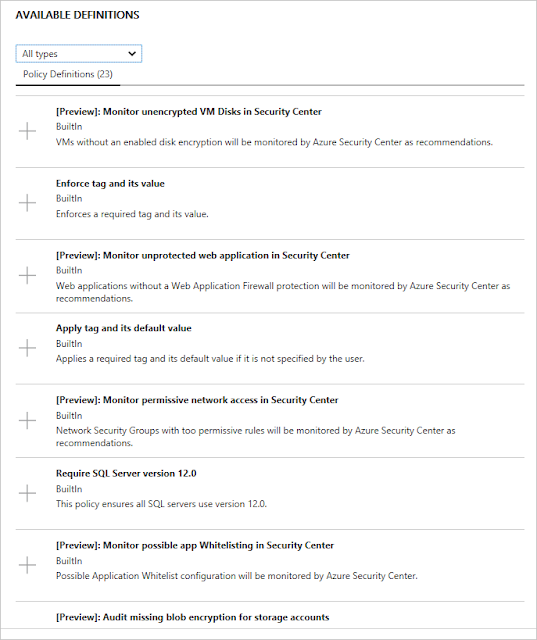
The Available Definitions window opens, displaying the default policy that's assigned to Security Center via Azure Policy.
7. (Optional) In the Available Definitions window, do either of the following:
◈ To add a policy definition, select the plus sign (+) next to the definition.
◈ For a detailed explanation of a policy, select it.
A definition Preview window opens. It displays a description of the definition and a link to the JSON code that provides the policy definition structure.
8. When you finish editing, select Save.
Available security policy definitions
To understand the policy definitions that are available in the default security policy, refer to the following table:
Policy
|
What the enabled policy does
|
System updates
|
Retrieves a daily list of available security and critical updates from Windows Update or Windows Server Update Services. The retrieved list depends on the service that's configured for your virtual machines, and it recommends that missing updates be applied. For Linux systems, the policy uses the distro-provided package-management system to determine packages that have available updates. It also checks for security and critical updates from Azure Cloud Services virtual machines.
|
Security configurations
|
Analyzes operating system configurations daily to determine issues that could make the virtual machine vulnerable to attack. The policy also recommends configuration changes to address these vulnerabilities. For more information about the specific configurations that are being monitored.
|
Endpoint protection
|
Recommends that endpoint protection be set up for all Windows virtual machines (VMs) to help identify and remove viruses, spyware, and other malicious software.
|
Disk encryption
|
Recommends enabling disk encryption in all virtual machines to enhance data protection at rest.
|
Network security groups
|
Recommends that network security groups be configured to control inbound and outbound traffic to VMs that have public endpoints. Network security groups that are configured for a subnet are inherited by all virtual-machine network interfaces unless otherwise specified. In addition to checking to see whether a network security group has been configured, this policy assesses inbound security rules to identify rules that allow incoming traffic.
|
Web application firewall
|
Recommends that a web application firewall be set up on virtual machines when either of the following is true:
|
Next generation firewall
|
Extends network protections beyond network security groups, which are built into Azure. Security Center discovers deployments for which a next generation firewall is recommended, and then you can set up a virtual appliance.
|
SQL auditing and threat detection
|
Recommends that auditing of access to Azure Database be enabled for compliance and advanced threat detection, for investigation purposes.
|
SQL encryption
|
Recommends that encryption at rest be enabled for your Azure SQL database, associated backups, and transaction log files. Even if your data is breached, it is not readable.
|
Vulnerability assessment
|
Recommends that you install a vulnerability assessment solution on your VM.
|
Storage encryption
|
Currently, this feature is available for Azure Blob storage and Azure Files. After you enable Storage Service Encryption, only new data is encrypted, and any existing files in this storage account remain unencrypted.
|
JIT network access
|
When just-in-time network access is enabled, Security Center locks down inbound traffic to your Azure VMs by creating a network security group rule. You select the ports on the VM to which inbound traffic should be locked down.
|






0 comments:
Post a Comment