We announced general availability of Azure SQL Data Warehouse (SQL DW) Compute Optimized Gen2 tier, the new generation of Azure SQL DW. Azure SQL DW is a fast, flexible, and secure cloud data warehouse tuned for running complex queries fast and across petabytes of data.
We see two key trends that drive data warehousing decisions, the amount of data continues to grow exponentially and the need to deliver insights from all this data is even more urgent. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier is designed to help customer accomplish just this by delivering dramatic query performance improvement. In addition, SQL DW now supports up to 128 concurrent queries while being able to provision five times more computing power compared to the previous product generation.
“After upgrading to the Gen2 of SQL Data Warehouse, our data warehouse workload has seen an average of 5.4 times performance improvement. This enhancement to the service is phenomenal and helps us deliver key customer insights for our business” said Brent Niezgocki, Senior Software Engineer for the Azure Active Directory analytics team at Microsoft.
We see two key trends that drive data warehousing decisions, the amount of data continues to grow exponentially and the need to deliver insights from all this data is even more urgent. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier is designed to help customer accomplish just this by delivering dramatic query performance improvement. In addition, SQL DW now supports up to 128 concurrent queries while being able to provision five times more computing power compared to the previous product generation.
“After upgrading to the Gen2 of SQL Data Warehouse, our data warehouse workload has seen an average of 5.4 times performance improvement. This enhancement to the service is phenomenal and helps us deliver key customer insights for our business” said Brent Niezgocki, Senior Software Engineer for the Azure Active Directory analytics team at Microsoft.
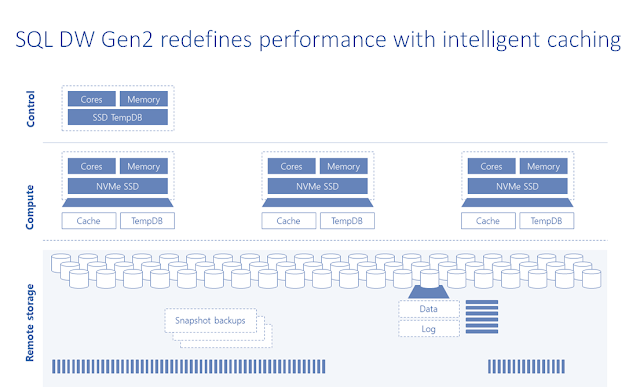
Fast query performance through adaptive caching
As organizations look to accelerate time to insight, performance in the domain of interactive queries continues to be a top requirement. One of the biggest bottlenecks and pain points for delivering high performance is disk access. This holds especially true in cloud computing where the distance from the compute layer to the storage layer can potentially vary, leading to suboptimal query performance. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier delivers built-in adaptive caching that automatically caches data based on workload characteristics and query access patterns. Combining in-memory and disk-deployed caches, SQL Data Warehouse automatically and transparently moves frequently accessed data across various caching tiers. This caching strategy leads to faster data access and ultimately faster query performances. In addition to smart caching strategies, Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier now leverages the latest hardware innovations that Azure offers. Together, all of this enables Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier to deliver the next level of performance characteristics. On average, query workloads see five times the performance improvements compared to SQL DW Gen1.
Powering enterprise-wide dashboards with high concurrency
Many organizations rely on Business Intelligence (BI) tools to get insight into various business metrics and KPIs. However, existing data warehousing systems typically limit the number of concurrent queries that can be processed and executed, leading to suboptimal user experiences. Organizations are forced to place tight control over valuable data stored in their data warehouses, or to limit how many users can simultaneously query their data warehouses. These circumstances lead to analysis delays.
Not anymore, Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier increases the number of concurrent queries that can be executed. With support for 128 concurrent queries, Azure SQL DW delivers four times more concurrency compared to the previous generation. This improvement allows organizations to satisfy the most demanding needs of their business and data analysts. To enable new concurrency levels, workload management functionality has been extended. Each SQL Data Warehouse SLO comes with predefined query capacity quotas. As the query concurrency grows, available capacity is consumed until the quota is reached. All this is happening completely transparently to the data warehouse end users, allowing your data warehouse to be used by hundreds of users who are using their BI tool of choice.
In the picture below, we see system throughput under the concurrency. Various queries were submitted to the system with 30s delay from each other. We see that number of active queries grows to 128, stays there for some time and ultimately drops down to zero as queries complete execution. While SQL DW was processing active queries, few queries were queued until resources became available for them to be processed.
Predictable performance through scaling
Organizations have been faced with an ever-growing demand to store and operate on larger and larger data sets. The ability to grow and shrink your data warehouse elastically, as your data needs to grow and shrink, is one of the key characteristics of SQL Data Warehouse. Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier enables two additional capabilities in this area, the ability to store unlimited data in SQL’s columnar format, and the availability of new SLOs with an additional five times the compute capacity.
SQL Data Warehouse now delivers unlimited columnstore storage capacity. With this new capability, you might wonder if there is enough compute power to deliver acceptable query performances on larger and larger data. To allow for effective data processing and to deliver predictable performances for growing data, Azure SQL DW Compute Optimized Gen2 tier increases the compute power by introducing additional SLOs (DW7500c, DW10000c, DW15000c and DW30000c).
To demonstrate the effects of scaling to these new SLOs, the picture below shows execution times after running the same set of queries over the same data while varying the SLOs. These three queries were executed on DW6000c and DW15000c respectively. We see that execution times improved with using higher SLO level (lower bar indicates response time improvement). The queries used exercise common analytical query patterns such as aggregations, joins, predicates, in clauses, subselects, and data ordering.







0 comments:
Post a Comment