Cloud computing and digital transformation have been powerful enablers for genomics. Genomics is expected to be an exabase-scale big data domain by 2025, posing data acquisition and storage challenges on par with other major generators of big data. Embracing digital transformation offers a practically limitless ability to meet the genomic science demands in both research and medical institutions. The emergence of cloud-based computing platforms such as Microsoft Azure has paved the path for online, scalable, cost-effective, secure, and shareable big data persistence and analysis with a growing number of researchers and laboratories hosting (publicly and privately) their genomic big data on cloud-based services.
At Microsoft, we recognize the challenges faced by the genomics community and are striving to build an ecosystem (backed by OSS and Microsoft products and services) that can facilitate genomics work for all. We’ve focused our efforts on three main core areas—research and discovery in genomic data, building out a platform to enable rapid automation and analysis at scale, and optimized and secure pipelines at a clinical level. One of the core Azure services that has enabled us to leverage high performance compute environment to perform genomic analysis is Azure CycleCloud.
Galaxy and Azure CycleCloud
Galaxy is a scientific workflow, data integration, and data analysis persistence and publishing platform that aims to make computational biology accessible to research scientists that do not have computer programming or systems administration experience. Although it was initially developed for genomic research, it is largely domain agnostic and is now used as a general bioinformatics workflow management system. Galaxy system is used for accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research.
◉ Accessible: Programming experience is not required to easily upload data, run complex tools and workflows, and visualize results.
◉ Reproducible: Galaxy captures information so that you don't have to; any user can repeat and understand a complete computational analysis, from tool parameters to the dependency tree.
◉ Transparent: Users share and publish their histories, workflows, and visualizations via the web.
◉ Community-centered: Inclusive and diverse users (developers, educators, researchers, clinicians, and more) are empowered to share their findings.
Azure CycleCloud is an enterprise-friendly tool for orchestrating and managing high-performance computing (HPC) environments on Azure. With Azure CycleCloud, users can provision infrastructure for HPC systems, deploy familiar HPC schedulers, and automatically scale the infrastructure to run jobs efficiently at any scale. Through Azure CycleCloud, users can create different types of file systems and mount them to the compute cluster nodes to support HPC workloads. With dynamic scaling of clusters, the business can get the resources it needs at the right time and the right price. Azure CycleCloud automated configuration enables IT to focus on providing service to the business users.
Deploying Galaxy on Azure using Azure CycleCloud
Galaxy is used by most academic institutions that conduct genomic research. Most institutions that already use Galaxy want to stick to it because it provides multiple tools for genomic analysis as a SaaS platform. Users can also deploy custom tools onto Galaxy.
Galaxy users generally use the SaaS version of Galaxy as part of UseGalaxy resources. UseGalaxy servers implement a common core set of tools and reference genomes and are open to anyone to use. All information on its usage is available on the Galaxy Platform Directory.
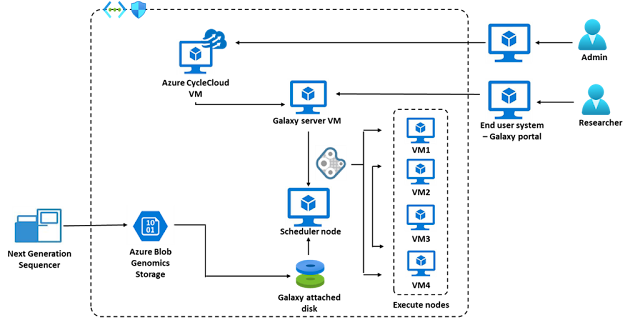
However, there are some research institutions that intend to deploy Galaxy in-house as an on-premises solution or a cloud-based solution. The remainder of this article describes how to deploy and run Galaxy on Microsoft Azure using Azure CycleCloud and grid engine cluster. The solution was built during the Microsoft hackathon (October 12 to 14, 2021) with code implementation assistance from Azure HPC Specialist, Jerry Morey. The architectural pattern described below can help organizations to deploy Galaxy in an Azure environment using CycleCloud and a scheduler of choice.





0 comments:
Post a Comment